Green Deindustrialization Comes to America
Play Stupid Games, Win(d and solar) Stupid Prizes
A growing number of articles have detailed how soaring energy prices are crippling heavy industry in Germany and several other European countries. The nascent deindustrialization of Europe stems from decades of bad energy policies mandating massive malinvestments in wind, solar, and Russian natural gas.
Unfortunately, some areas of the United States that have pursued similar energy policies—sans the Russian gas—are beginning to experience their own “green deindustrialization.” To make matters worse, rather than reevaluating these policies in light of the troubles in Europe, many U.S. policymakers are doubling down on the same failed policies that have brought us to this point in the first place.
End of the Line
For example, on Friday, March 1st, 2024, Indiana-based Metal Technologies Incorporated (MTI) announced it would be closing its Northern Foundry facility located in Hibbing, Minnesota—the hometown of Bob Dylan— due to the state's surging electricity costs. The Minneapolis-Star Tribune reports:
"Electricity cost is a major expense," MTI said in a news release. "Minnesota Power's repeated electricity rate increases ... mean Northern Foundry pays substantially more per kilowatt hour than MTI's other facilities."
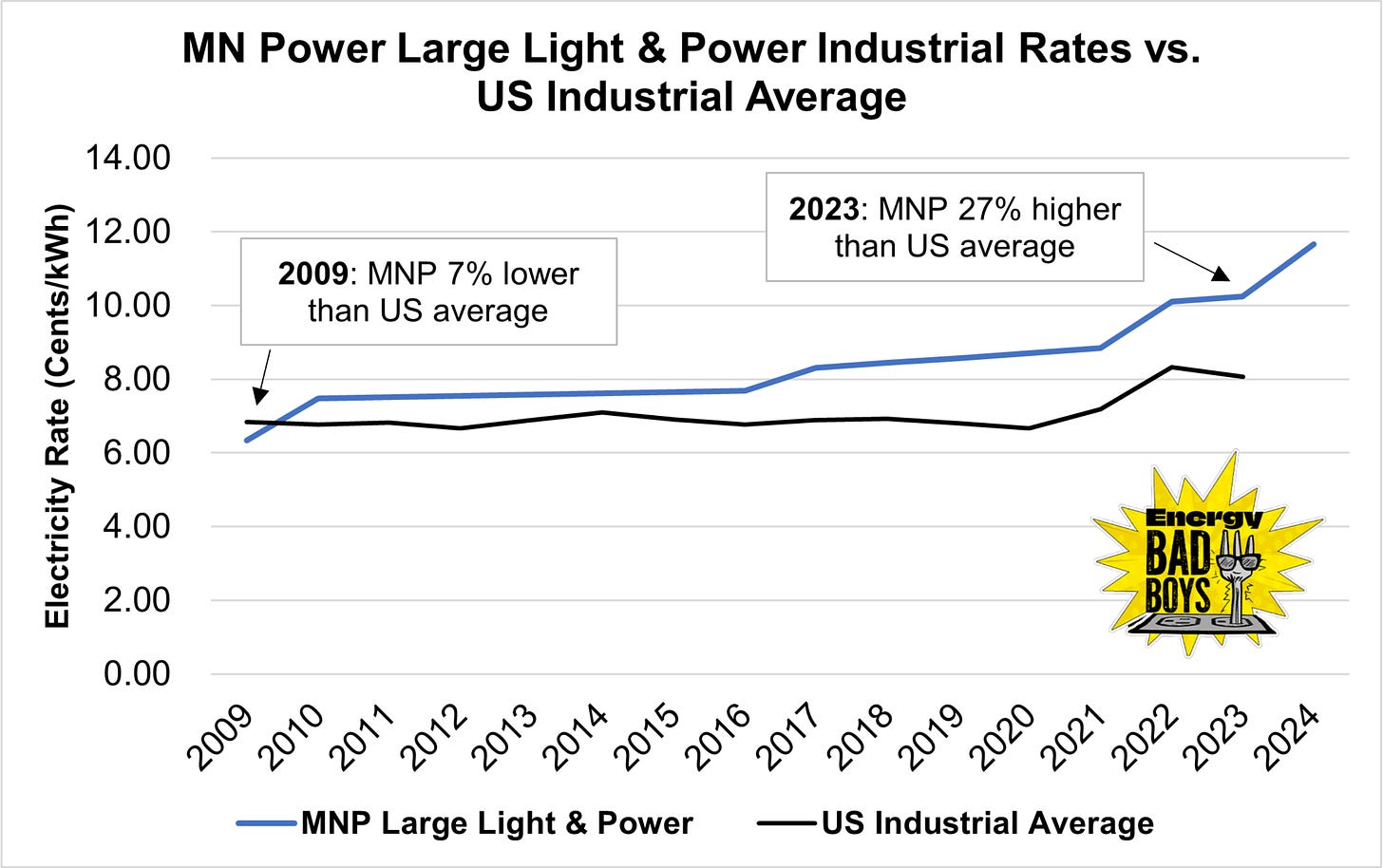
From 2009 to 2023, Minnesota Power, the Investor-Owned Utility that served Northern Foundry, has increased electricity prices for industrial customers like the foundry by 62 percent, compared to the US average increase of only 18 percent, making it increasingly difficult for energy-intensive businesses to compete with firms in other states and countries with more rational energy policies.
Northern Foundry was the definition of an energy-intensive business. The firm used electric induction furnaces to melt ductile iron into parts used for the automotive, heavy truck, industrial, and recreational industries. When operating at full capacity, the facility consumed six megawatts (MW) of power, equivalent to the average consumption of 5,660 Minnesota homes.
In an average year, this facility would likely use more than 30,000 megawatt-hours (MWh) of electricity every year, and as rates have risen, the rising prices increased Northern Foundry’s costs by an estimated $1.2 million, or about 27 percent of the company’s payroll. Ultimately, they saw the writing on the wall and closed up shop for good.
"Green Energy" Kills Good Jobs
It seems we are constantly told that enacting "green energy" policies will create a panacea of good-paying jobs, but the Energy Bad Boys have been warning for years that Minnesota’s mandates for unreliable wind and solar would drive up costs and destroy thousands of the high-paying jobs we already have.
It was only a matter of time before these warnings became a reality.
The closure of Northern Foundry means 91 people no longer have jobs. These jobs were also union jobs, as the employees at the facility were members of the United Steelworkers Union. The average annual pay for employees was around $48,900, with opportunities for overtime, healthcare benefits including dental and vision, 401k contributions, and even a match for 529 college savings plans, so workers could save money and invest it to pay for their children’s educations.
While $48,900 may not seem like much for people living in urban areas, in Hibbing, this is a very good wage. The U.S. Census Bureau estimates the median household income in Hibbing is $52,881, meaning one person working at Northern Foundry was almost making as much as the average household in the area.
These are the kinds of jobs that are emblematic of the American Dream, where hard work allows everyday people to earn good wages, buy a house, and put their kids through school. Members of the American Left used to appreciate these jobs, but the energy policies they now champion are pricing them out of existence.
Renewables Are Increasing Rates
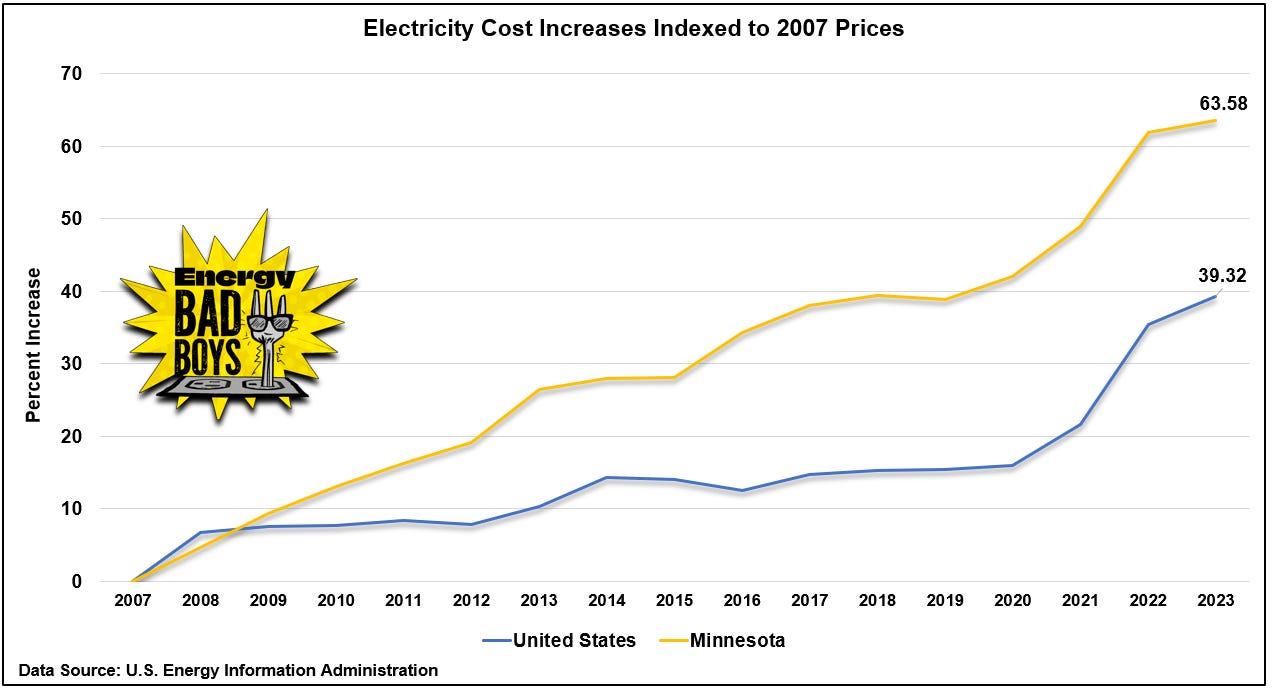
In 2007, Minnesota became an early adopter in mandating the use of wind and solar on the state’s electric grid, passing the Next Generation Energy Act (NGEA). This legislation mandated that 25 percent of Minnesota’s electricity come from “renewable” resources by 2025, and it has caused electricity prices to soar.
For example, Minnesota’s all-sectors electricity rates were once 18 percent below the national average in 2007, but since the NGEA was passed, Minnesota’s electricity prices have increased 1.6 times faster than the national average, which you can see in the graph below.
While the NGEA was the initial catalyst for rising rates, IOUs in the state soon saw wind and solar as a way to bolster their corporate profits by building new infrastructure to put into their ratebase.
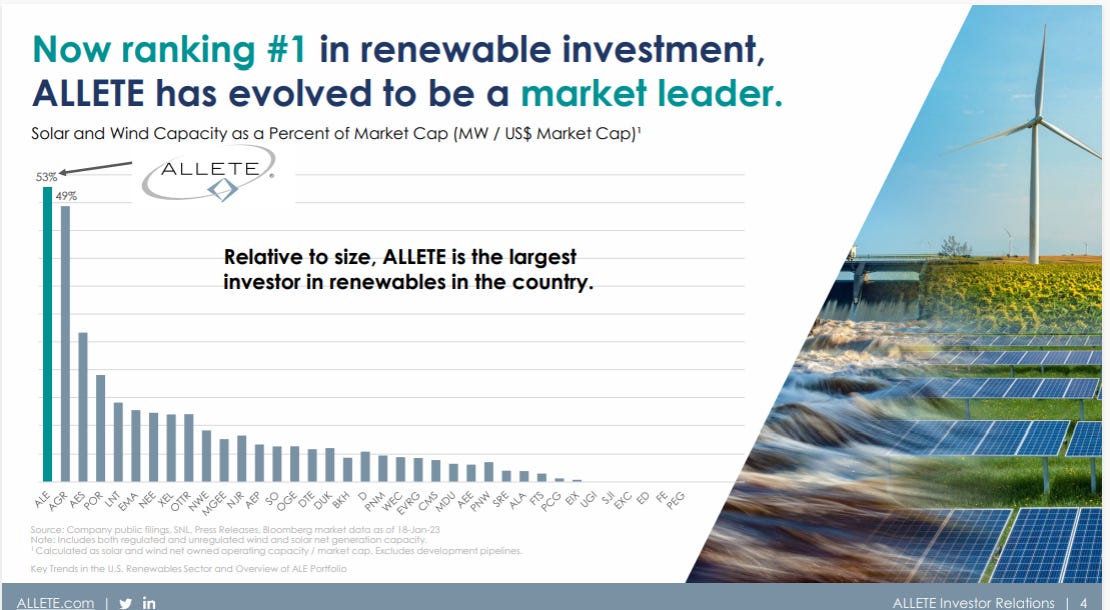
This is why companies like Xcel Energy and Allete Energy —the parent company for Minnesota Power— announced they would go above and beyond the mandates for renewable energy with their own company-wide pledges.
Unfortunately, these efforts were codified when Minnesota passed a 100 percent carbon-free electricity mandate by 2040 that did not lift the state’s ban on building new nuclear power plants. Now, Allete brags about how much money they spend on renewables in their shareholder documents:
“Our updated five-year capital expenditure plan of $4.3 billion reflects the tremendous growth opportunities at Minnesota Power. We’ve added approximately $1 billion to our previous plan, reflecting the significant investments in regulated renewable and transmission projects necessary to advance a clean-energy future and meet state carbon-free energy goals.
While nice for Minnesota Power’s shareholders, these renewable investments haven’t been very beneficial for its customers, as they are the primary drivers behind recent price hikes at Minnesota Power and have led industrial companies like the Hibbing Northern Foundry to lay off 91 people.
As Minnesota Power stated in its 2023 rate increase request to the Minnesota Public Utilities Commission (MPUC), under the section “Description and need for interim rates”:
Minnesota Power has transformed its generation fleet and added other internal resources that will assist Minnesota Power in achieving the state of Minnesota’s new goal of providing 100 percent carbon-free electricity by 2040; modernizing its transmission grid to facilitate the delivery of renewable energy; and supporting enhanced customer offerings and conservation opportunities…
Overall, Minnesota Power requires interim rates due to changes in revenue and in its overall cost of providing reliable customer service while leading efforts toward decarbonization… Without interim rate relief, Minnesota Power would be unable to recover its reasonable costs of providing electric service to its customers, and would not have a reasonable opportunity to earn its authorized rate of return.
In 2021, Xcel Energy, the utility company with the most expensive electricity rates in the state, sang a similar tune in its request to raise electricity prices on customers:
Xcel Energy seeks authority to increase electric rates, through a three-year multiyear rate plan (MYRP), to reflect the cost of providing service to our customers, including an appropriate return on common equity… The MYRP we propose builds on the success of the 2016-2019 MYRP and will allow the Company to continue providing leadership on a number of key initiatives, including: (1) expanding our renewable energy portfolio and further transforming our generation fleet as we lead the clean energy transition; (2) creating an advanced distribution grid to better serve our customers and enable further transformation of our overall energy delivery system; and (3) assisting in continued beneficial electrification.
Clearly, investments in pursuit of Minnesota’s carbon-free mandates are directly responsible for electricity rate increases in the state that far exceed the national average and are being used by regulated utility monopolies to bolster their profits at the expense of their ratepayers.
Broader implications
States that are the most aggressive in mandating unreliable wind and solar will see less investment than smarter states. Due to the partisan nature of these mandates, the states enacting them likely have other business disadvantages, as well, including larger regulatory burdens and more taxes.
It’s no surprise that many of the largest manufacturing projects are accruing to states with fewer mandates for unreliable energy sources. To the extent that companies are building in Blue states with 100 percent carbon-free mandates, it has partially been influenced by lucrative targeted tax breaks and other financial incentives.
For example, In Michigan, state lawmakers committed to giving Ford $1.7 billion from Michigan taxpayers to build its BlueOval Battery Park in Marshall, which will be paid through direct cash giveaways and tax abatements. Incentives like these will become even more necessary due to Michigan’s recently passed 100 percent-carbon free electricity mandate that will make heavy industry less viable in the future.
The Rural-Urban Divide
The loss of Northern Foundry in Hibbing is emblematic of a growing urban-rural divide where the “green” policies enacted by affluent, liberal city folk undermine the economic viability of rural areas. Not only are rural residents expected to happily host the thousands of wind turbines and solar panels mandated onto the electric grid, but rural economies are also disproportionately harmed by rising energy prices due to the energy-intensive nature of their industries.
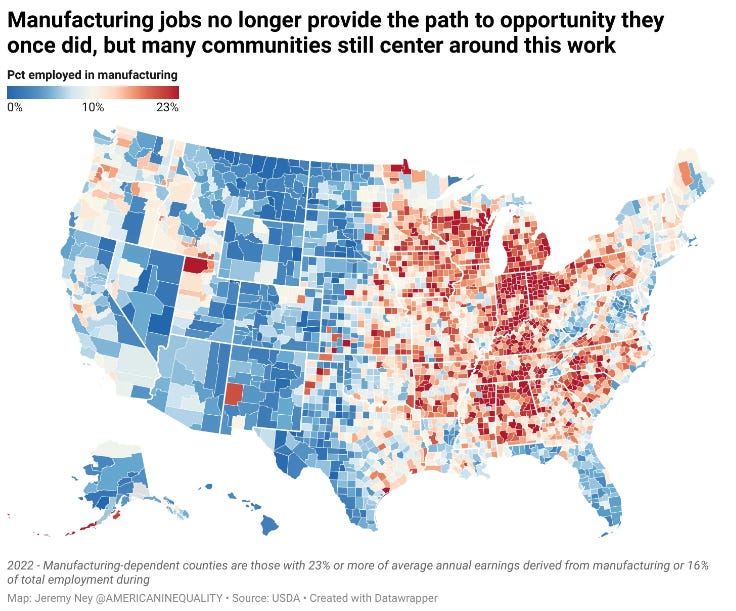
In the case of manufacturing jobs, urban areas of the United States have more manufacturing jobs overall, but manufacturing jobs are often more important to the economy in rural areas because one or two manufacturing firms can be the bedrock on which the rest of the economy in rural communities is built. If these jobs go away, the ripple effects on the rest of the community are significant, as people have less money to support local grocery stores, bakeries, hospitals, and schools.
The map below from
uses U.S. Census data to show the percentage of people employed in manufacturing in each county in the United States. Blue areas have a smaller portion of their population in the industry, and red areas have more people working in it.In states with high amounts of manufacturing, like Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, and Wisconsin, you’ll often see lighter colors near the population centers in Chicago, Indianapolis, Lansing, Minneapolis/St. Paul, Columbus, and Madison, as jobs in the service industry are more prevalent.
The residents of these areas also tend to more strongly favor mandating expensive wind and solar facilities because they have higher wages and can afford the “green premium” they pay to feel good about their choices, and they are less reliant on energy-intensive industries for their livelihoods, which means it won’t be their job that disappears because of these policies.
Conclusion
We should all be grateful that Metal Technologies has said the quiet part out loud: rising electricity prices are already causing heavy industry to rethink their investments in high-cost states.
Other companies are likely running the numbers and coming to similar conclusions, but they are not as willing to say the quiet part out loud due to concerns about Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG) impacts, which means they will quietly invest in lower-cost areas while communities like Hibbing suffer the consequences.
The saddest part about this entire situation is that it was entirely foreseeable and occurred largely because of the poor policy decisions made in the state. As a result, 91 families didn’t need to learn that they’ll soon be out of a job.
Hopefully, the loss of the Northern Foundry can serve as a warning sign to policymakers so they understand that enacting the same policies as Europe and expecting different results is a recipe for green deindustrialization.
Please like, subscribe, and share this post so we can deindustrialize the wind and solar industrial complex!
Here’s what we’ve been reading this week:
The Political Economy of EPA’s Updated Social Cost of Carbon by
Did An American Grid Operator Just Deny Climate Change? by
Biden EPA Adjusting Costly Green Power Plants Scheme To Hedge Against Legal Challenges by Nick Pope







My recent conversations on LinkedIn about Mitch Rolling's recent post come to mind. When crossing swords with a avid renewable supporter, they will always pull that the Midwest states are mostly wind have the lowest rates out of their playbook. What they skip over is which states have 100% mandated green energy and that effect on rates. While it's true the renewable subsidies are effecting reliability everywhere, their upward pressure on energy prices has been muted (for now) in fully competitive markets. Your article does an eloquent job of showing what happens as soon as a state jumps on the green train. It should create quite a stir on LinkedIn.
With 3 of MTIs other 5 plants being in Michigan, how long before those 3 close also leaving one remaining plant in Indiana and one in Mexico?